
sarbodayanepaljumla@gmail.com
9858320498
SARBODAYA Development for Campaign Nepal (SARBODAYA Nepal) Jumla has launched its strategic plan for 2025-2030, building on extensive learnings from past projects, stakeholder feedback, and environmental analysis. This strategy prioritizes addressing critical challenges in Gender-Based Violence (GBV), gender-sensitive food security and livelihoods, environment and biodiversity conservation, WASH and nutrition services, and disaster risk reduction with a focus on climate resilience. It aims to strengthen existing networks and create new partnerships, positioning SARBODAYA Nepal as a leader and facilitator in participatory GBV and gender inclusion development, particularly within agriculture, climate change, biodiversity, and natural resource sectors. Promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion through quality program and service delivery remains a core commitment.
Notably, a new collaboration was established with UN Women for the "Hamra Sahas Project," operating across six municipalities in Jumla district, focusing on women's empowerment and resilience. Additionally, Sarbodaya Nepal expanded its role through a landscape strategy planning study under the UNDP - GEF Small Grants Programme (SGP). This consultative initiative supports sustainable landscape management across provinces such as Lumbini, Gandaki, Koshi, and Sudurpaschim, covering districts including Jumla, Kalikot, Dailekh, Achham, Lamjung, Rupandehi, and Terhathum.
SARBODAYA Nepal continued to reinforce its organizational framework by reviewing and updating key policies, including Human Resources, Procurement Procedures (revised 2025), and the Preventing Sexual Exploitation and Abuse (PSEA) Policy of 2025, enhancing its governance and safeguarding measures in the workplace.
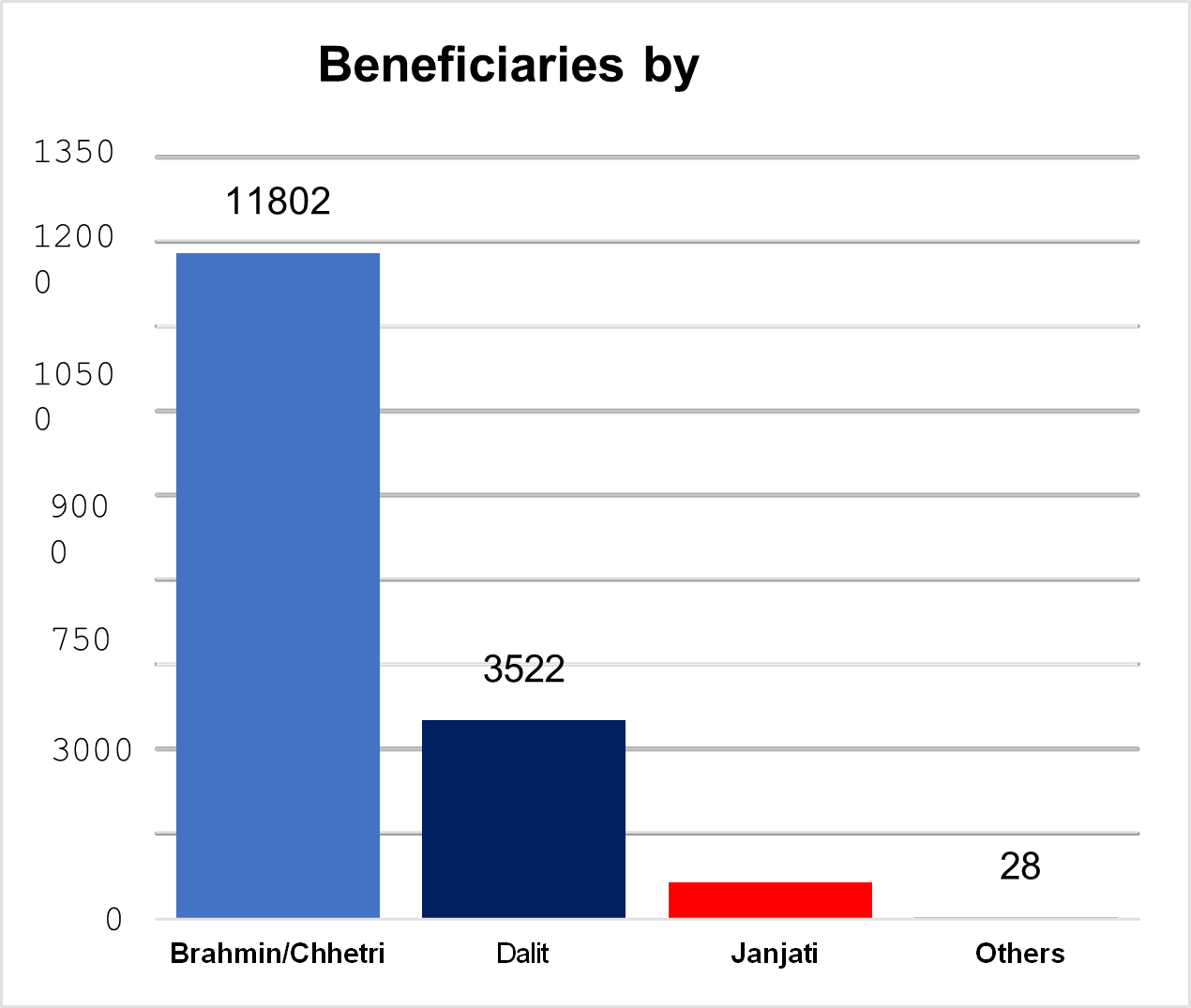
Operationally, Sarbodaya Nepal implemented six key projects during the year, directly benefiting 15,991 households. Of these beneficiaries, 79%
were women (12,637) and 21% men (3,354). Demographically, the beneficiaries comprised 74% Brahmin/Chhetri, 22% Dalit and Janajati, 4% other Janajati groups, and 0.2% from other communities. These efforts demonstrate to inclusive development and its impact across diverse social groups.